ROLE OF XYLEM AND PHLOEM
Collenchyma and sclerenchyma have lignified cell.This lignification becomes the reason of hardness.
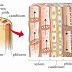
- Collenchyma is present in cortex ans sclerenchyma in xylem tissues.
- The stems of land plants resist against wind.
- Bending is checked by xylem.
- Xylem tissues play role like steel road.
In short, the arrangement of vascular bundles in the rings provides resistance to wind stress, and weight bearing ability.
ROLE OF SCLERENCHYMA
- Generally, these cells are non-living.
- Sclerenchyma cells provide support to the plant parts.
- They are rigid due to secondary cell walls.
- Lignin makes the wall tough ang rigid.
There are three types of sclerenchymatous cell:
(i) Fiber
(ii) Sclerids (Stone cells)
(iii) Vessels (Trachea)
FIBERS: These are long and cylindrical. They are found in solid bundles in xylem or as bundle caps. Fibers are common in plant stems.
SCLERIDS (Stone cells): There are common in shells of nuts and seed coats.
Sclerids are shorter than fiber. They give strength.
VESSELS (Trachea): These are long tubular structures.
These structure are joined end to end and form long water conducting pipe in xylem.
ROLE OF COLLENCHYMA
(i)_The outer most cells of the cortex of young stems, lying just beneath the epidermis,often constitute a tissue known as collenchyma.
(ii)_The walls of collenchyma cells are composed of layers of pectin and cellulose.
The cell walls are thickened at the corner.
(iii)_These thickenings are flexible these tissues form complete cylinder.
(iv)_Collenchyma cells provide support to herbaceous parts of the plants.
(v)_Cells are also found in petioles of leaves.
(vi)_Protoplasm remains alive.
(vii)_These cells are without secondary wall.
Role of Xylem Phloem, Sclerenchyma, Collenchyma
 Reviewed by SaQLaiN HaShMi
on
11:56 PM
Rating:
Reviewed by SaQLaiN HaShMi
on
11:56 PM
Rating:
 Reviewed by SaQLaiN HaShMi
on
11:56 PM
Rating:
Reviewed by SaQLaiN HaShMi
on
11:56 PM
Rating:







No comments: