SECTION - III
Attempt any THREE questions: (8 x 3 = 24)
Q.5
(a) Explain the structure and function of cell wall?
Ans. CELL WALL:
- The outer most boundary in most of the plant cells is cell wall.
- The cell wall of plant cell is different from that of prokaryotes, Both in structure and chemical composition.
- It is secreted by protoplasm of the cell.
- Its thickness varies in different cells of the plant.
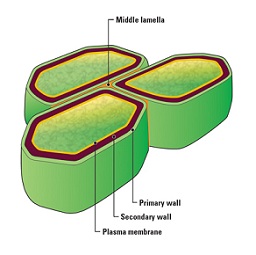
(1) Composition and Structure:
It is composed of three main layers:
- Primary wall
- Secondary wall
- Middle Lamella
(i) Middle Lamella:
The middle lamella is first to be formed in between the primary walls of the neighboring cells.
(ii) Primary Wall:
The primary wall is composed of :
- Cellulose and some deposition of
- Pectin (gelling agent) and
- Hemicelluloses
Cellulose molecules are arranged in a criss-cross arrangement. The primary wall is a true wall and develops in newly growing cells.
(iii) Secondary Wall:
The secondary wall is formed on its inner surface and is comparatively thick and rigid.
Chemistry it is composed of:
- Prokaryotic cell wall lacks cellulose; its strengthening material is peptidoglycan or Murein.
- Fungal cell wall contains chitin.
(2) Functions:
- Cell wall is very important.
- It provides a definite shape to the cell and keep it rigid.
- It does not act as a barrier to the materials passing through it.
Q.5
(b) Write importance of pea family?
Ans. ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE: (PEA FAMILY)
(i) High-Protein:
The family is of considerable importance as a source of high protein food, oil, and forage as well as ornamentals and other uses.
Main importance lies in the pulses, belonging to this family, which are used as food, some important and common species of pulses yielding plants are:
(b) Write importance of pea family?
Ans. ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE: (PEA FAMILY)
(i) High-Protein:
The family is of considerable importance as a source of high protein food, oil, and forage as well as ornamentals and other uses.
Main importance lies in the pulses, belonging to this family, which are used as food, some important and common species of pulses yielding plants are:
- Gram
- Pea
- Kidney bean
These pulses are rich in protein contents.
(ii) Forage Crop of Horses:
- (Medicago sativa) Alfalfa is one of the worlds best forage crop for horses.
(iii) Fodder Crops:
- Vicia. Melilotus and Trifolium are also cultivated as main fodder crops.
- Many trees of this family provide excellent timber for building, furniture and fuel.
- Main timber plants are Butea, Dilbergia etc.
(iv) Vegetable Oil:
Seeds of Arachis hypogea peanut are edible and also used for extraction of peanut oil which after hydrogenation is used as a vegetable oil.
(v) Indigo Dyes:
Indigo dyes are obtained from Indigofera tinctoria and Butea monosperma, yielding yellow dye from flowers.
(vi) Medicines:
- Many plants of this family are important for medicines.
- These include Glycyrrhiza glabra for cough and cold.
- Clitoria ternatea is used against snake bite.
(vii) Weights:
The red and white seeds of Abrus precatorious are used by jewelers as wights called "ratti".
(viii) Ornamental:
Some important ornamental plants include Lathyrus, Lupinus, Clitoria, Butea etc.
Explain the structure and function of cell wall?
 Reviewed by SaQLaiN HaShMi
on
9:09 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by SaQLaiN HaShMi
on
9:09 AM
Rating:
 Reviewed by SaQLaiN HaShMi
on
9:09 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by SaQLaiN HaShMi
on
9:09 AM
Rating:








No comments: